Understanding Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when your body either doesn't produce enough insulin or can't effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When diabetes is left unmanaged, it can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, blindness, and even amputations. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of diabetes, including its types, symptoms, causes, management, and prevention.
Types of Diabetes
1. Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body's immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This type of diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, which is why it is sometimes referred to as juvenile diabetes. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections to manage their blood sugar levels.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin. This type of diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor diet, and lack of exercise. While it is more common in adults, it is increasingly being diagnosed in younger individuals due to rising obesity rates.
3. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased demand. This type of diabetes usually resolves after childbirth, but it increases the mother's risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes may also be at higher risk for obesity and type 2 diabetes.
4. Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. It is a warning sign that you are at risk of developing diabetes and its complications if lifestyle changes are not made.
Symptoms of Diabetes
The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type and severity. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination: High blood sugar levels cause the kidneys to filter out more sugar, leading to increased urination.
- Excessive thirst: As the body loses fluids through frequent urination, it leads to dehydration and increased thirst.
- Fatigue: Without enough insulin, the body cannot effectively use glucose for energy, leading to constant fatigue.
- Unexplained weight loss: In type 1 diabetes, the body may start breaking down muscle and fat for energy due to a lack of insulin.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can cause the lens of the eye to swell, leading to blurred vision.
- Slow-healing wounds: High blood sugar levels can impair circulation and the immune system, leading to slow healing of cuts and wounds.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for a diagnosis.
Causes of Diabetes
Diabetes is a multifactorial disease, meaning it can be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes increases the risk of developing the condition. Specific genes may make individuals more susceptible to diabetes.
- Obesity: Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Fat tissue can release chemicals that disrupt the body's insulin sensitivity.
- Lack of physical activity: A sedentary lifestyle contributes to weight gain and insulin resistance, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Unhealthy diet: Consuming a diet high in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and processed foods can lead to obesity and insulin resistance.
- Age: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, especially after 45 years old.
- Other medical conditions: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and high blood pressure are associated with an increased risk of diabetes.
Managing Diabetes
Managing diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and monitoring. Here's how you can effectively manage diabetes:
1. Healthy Eating
A balanced diet is crucial for managing diabetes. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Avoid sugary drinks, refined carbs, and processed foods. Carbohydrate counting can also help manage blood sugar levels by monitoring the number of carbs consumed.
2. Regular Exercise
Physical activity helps the body use insulin more efficiently, which can lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Strength training exercises can also help build muscle and improve insulin sensitivity.
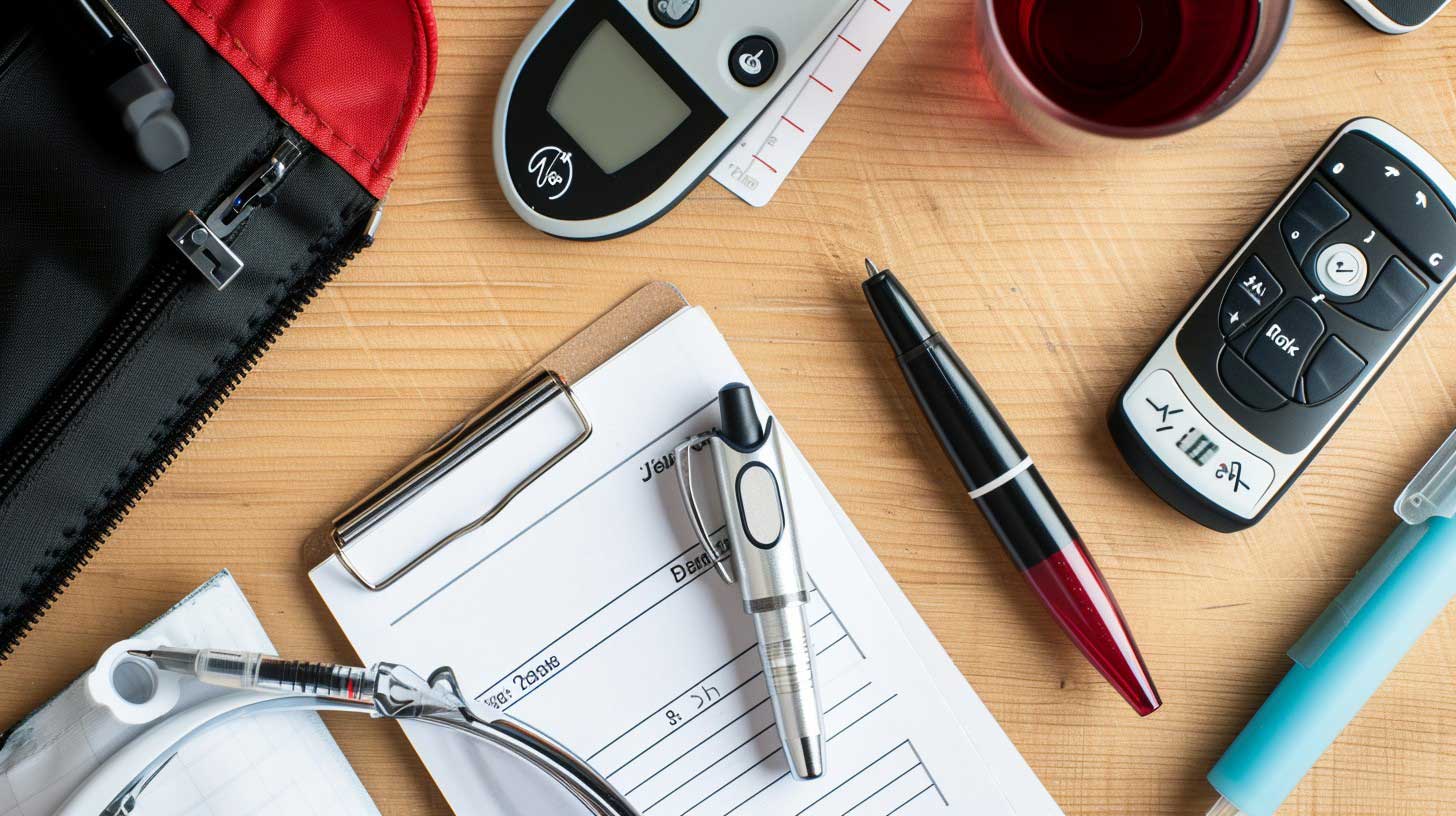
3. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing diabetes. This can be done using a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor (CGM). Keeping track of your levels helps you understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect your blood sugar.
4. Medication and Insulin Therapy
For some individuals, lifestyle changes alone may not be enough to manage diabetes. In such cases, medications like metformin or insulin therapy may be necessary. Your healthcare provider will work with you to determine the best treatment plan.
5. Stress Management
Chronic stress can lead to elevated blood sugar levels. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, and regular physical activity can help manage stress and improve overall well-being.
6. Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your diabetes and preventing complications. This includes routine blood tests, eye exams, and foot exams.
Preventing Diabetes
Prevention is key when it comes to diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes. Here are some strategies to reduce your risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight and maintaining a healthy BMI can significantly reduce your risk of diabetes.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Avoid sugary snacks and beverages.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity can help you maintain a healthy weight and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of diabetes and its complications. If you smoke, seek support to quit.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to weight gain and insulin resistance, increasing the risk of diabetes.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a complex and potentially life-threatening condition, but it can be managed with the right approach. By understanding the different types of diabetes, recognizing the symptoms, and making necessary lifestyle changes, you can take control of your health. Early diagnosis and consistent management are key to preventing complications and leading a healthy, fulfilling life.
If you are at risk or have been diagnosed with diabetes, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options. Remember, managing diabetes is a lifelong commitment, but with the right tools and support, it is entirely possible to live a healthy and active life.
Explore: Understanding Vitamin Deficiencies: Symptoms, Causes, and How to Increase Vitamin Levels